Corte con los ejes de coordenadas
Calcula los puntos de corte con los ejes de coordenadas de las siguientes funciones:
– a) ![]()
– b) ![]()
– c) ![]()
– d) 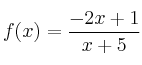
– e) 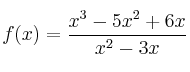
– f) 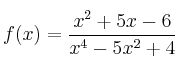
– g) ![]()
– h) ![]()
SOLUCIÓN
Para calcular los puntos de corte hacemos ![]() y calculamos
y calculamos ![]() (para el otro eje hacemos
(para el otro eje hacemos ![]() y calculamos
y calculamos ![]() )
)
– a) ![]()
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]()
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]()
– b) ![]()
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]()
![]() y
y ![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]() y
y ![]()
– c) ![]()
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]()
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]() ;
; ![]() ;
;![]() ;
; ![]()
– d) 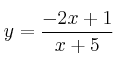
![]() . Corte
. Corte 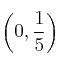
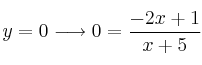
![]() .
.
Corte 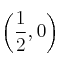
– e) 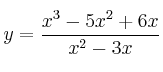
La función se puede simplificar quedando ![]()
Por tanto los puntos de corte son ![]() y
y ![]()
– f) 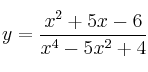
La función se puede simplificar quedando 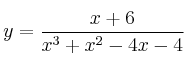
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]()
![]() . Corte
. Corte ![]()
– g) ![]()
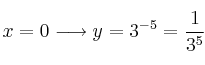 . Corte
. Corte 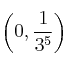
![]() (No tiene solución. No corta)
(No tiene solución. No corta)
– h) ![]()
![]() . (No corta. No existe logaritmo de número negativo)
. (No corta. No existe logaritmo de número negativo)
![]()
Corte ![]()