Dominio de una función
Calcula el dominio de las siguientes funciones:
– a) ![]()
– b) ![]()
– c) ![]()
– d) 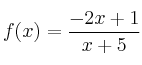
– e) 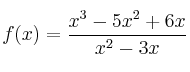
– f) 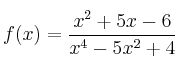
– g) ![]()
– h) ![]()
– i) ![]()
– j) ![f(x) = \sqrt[4]{x^2-5x+6} f(x) = \sqrt[4]{x^2-5x+6}](local/cache-TeX/e9e191119e0249588b43a43827057666.png)
SOLUCIÓN
– a) ![]()
![]() (por ser polinómica)
(por ser polinómica)
– b) ![]()
![]() (por ser polinómica)
(por ser polinómica)
– c) ![]()
![]() (por ser polinómica)
(por ser polinómica)
– d) 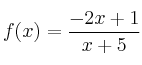
![]()
![]()
– e) 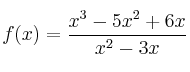
![]()
![]()
– f) 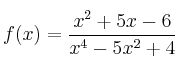
![]()
![]()
– g) ![]()
![]() (por ser exponencial)
(por ser exponencial)
– h) ![]()
![]()
![]()
– i) ![]()
![]()
![]()
– j)![f(x) = \sqrt[4]{x^2-5x+6} f(x) = \sqrt[4]{x^2-5x+6}](local/cache-TeX/e9e191119e0249588b43a43827057666.png)
![]() (resolvemos la inecuación de 2º grado y obtenemos como solución
(resolvemos la inecuación de 2º grado y obtenemos como solución ![]()
![]()